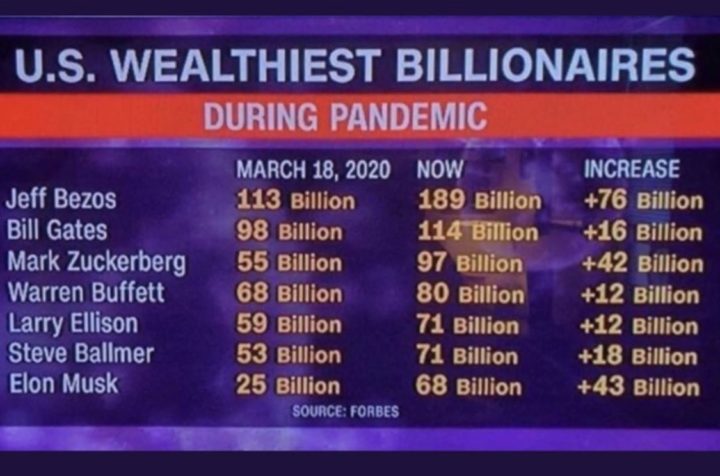
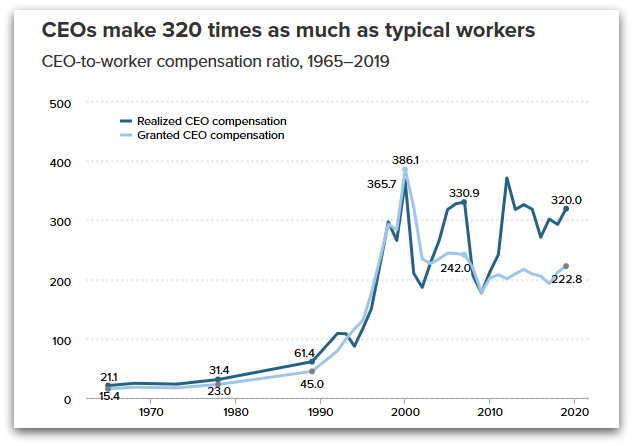
As Wages Stagnate and Executive Pay ‘Continues to Balloon,’ Report Shows Top CEOs Now Make 320 Times More Than Typical Worker
CAPITALISM, 24 Aug 2020
Jake Johnson | Common Dreams - TRANSCEND Media Service
New research from the Economic Policy Institute finds that CEO compensation grew by 1,167% from 1978 to 2019, “far outstripping” the growth of the stock market.
18 Aug 2020 – New research published today by the Economic Policy Institute shows that the top executives at the largest corporations in the United States now make 320 times more than what their typical employees earn in wages and benefits.
“CEO pay can be curbed to reduce the growing gap between the highest earners and everyone else with little, if any, impact on the output of the economy or firm performance.”
—Jori Kandra, Economic Policy Institute
EPI’s latest annual analysis of executive compensation finds that the CEOs of the top 350 firms in the U.S. raked in an average of $21.3 million in 2019, a 14% increase from 2018. The 320-1 ratio of CEO-to-worker pay in 2019 is more than five times higher than the 61-1 ratio reported in 1989.
The think tank’s research comes amid a global pandemic that is likely to exacerbate the decades-long trend of surging income and wealth inequality in the U.S.—a trend that, according to EPI, won’t be reversed by CEOs opting to take salary cuts during a public health crisis that has left tens of millions of Americans jobless.
EPI’s new report shows that CEO compensation grew by 1,167% from 1978 to 2019, “far outstripping” the growth of the stock market.
“CEOs who volunteer to take salary cuts aren’t giving up a lot given how much of their pay comes from stock awards and options,” EPI said.
Lawrence Mishel, a distinguished fellow at EPI and co-author of the new report, said in a statement that “while wage growth for the majority of Americans has remained relatively stagnant for decades, CEO compensation continues to balloon.”
“This has fueled the spectacular income growth of the top 0.1% and 1.0% and the growth of income inequality overall,” said Mishel, who told the Washington Post that CEO pay could rise again in 2020 despite the nationwide economic collapse caused by the Covid-19 crisis.
“CEOs offering salary cuts during the coronavirus pandemic yield press releases,” Mishel added, “but no real progress toward reducing inequality and raising workers’ wages.”
As a substantive alternative to CEO public relations stunts, EPI proposed several policy changes that would significantly reduce the yawning gap between CEO compensation and typical worker pay:
- Reinstating higher marginal income tax rates at the very top of the income ladder;
- Setting corporate tax rates higher for firms that have higher ratios of CEO-to-worker compensation;
- Capping compensation and tax anything over the cap; and
- Allowing greater use of “say on pay,” which allows a firm’s shareholders to vote on top executives’ compensation.

A demonstrator holds a “Tax the Rich” sign during a protest in New York on June 27, 2020. (Photo: Erik McGregor/LightRocket via Getty Images)
Jori Kandra, research assistant at EPI and co-author of the new report, said the “huge growth in CEO pay” over the past four decades “is not a reflection of the market for talent.”
“We know this because CEO compensation has grown more than three times faster than the growth of earnings for the top 0.1% of earners, which was 337% over the same period,” said Kandra. “This means that CEO pay can be curbed to reduce the growing gap between the highest earners and everyone else with little, if any, impact on the output of the economy or firm performance.”
____________________________________________
Jake Johnson is a staff writer for Common Dreams.
Tags: Capitalism, Corruption, Elites, Finance, Inequality, Mafia, Super rich
DISCLAIMER: The statements, views and opinions expressed in pieces republished here are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of TMS. In accordance with title 17 U.S.C. section 107, this material is distributed without profit to those who have expressed a prior interest in receiving the included information for research and educational purposes. TMS has no affiliation whatsoever with the originator of this article nor is TMS endorsed or sponsored by the originator. “GO TO ORIGINAL” links are provided as a convenience to our readers and allow for verification of authenticity. However, as originating pages are often updated by their originating host sites, the versions posted may not match the versions our readers view when clicking the “GO TO ORIGINAL” links. This site contains copyrighted material the use of which has not always been specifically authorized by the copyright owner. We are making such material available in our efforts to advance understanding of environmental, political, human rights, economic, democracy, scientific, and social justice issues, etc. We believe this constitutes a ‘fair use’ of any such copyrighted material as provided for in section 107 of the US Copyright Law. In accordance with Title 17 U.S.C. Section 107, the material on this site is distributed without profit to those who have expressed a prior interest in receiving the included information for research and educational purposes. For more information go to: http://www.law.cornell.edu/uscode/17/107.shtml. If you wish to use copyrighted material from this site for purposes of your own that go beyond ‘fair use’, you must obtain permission from the copyright owner.