Bija Swaraj Not Bt Raj: The Future Is Organic, Not GMOs
TRANSCEND MEMBERS, 31 Aug 2015
Dr Vandana Shiva – TRANSCEND Media Service
 31 Aug 2015 – Farmers, first of all, are breeders. They might not have the lab coats that have come to define modern plant breeding, but their wisdom, knowledge and contribution is unquestionable. To be able to continue breeding, using their own seed, is their first right, their first freedom and their first duty.
31 Aug 2015 – Farmers, first of all, are breeders. They might not have the lab coats that have come to define modern plant breeding, but their wisdom, knowledge and contribution is unquestionable. To be able to continue breeding, using their own seed, is their first right, their first freedom and their first duty.
This right has been recognised in India’s Plant Variety Protection and Farmers Rights Act
39 (iv) a farmer shall be deemed to be entitled to save, use, sow, resow, exchange, share or sell his farm produce including seed of a variety protected under this Act in the same manner as he was entitled before the coming into force of this Act :
All seeds bred by the public sector or by private corporations are based on varieties bred by farmers.
For the last 2 decades, Monsanto has forcefully monopolised the cotton seed sector with its Bt Cotton seeds, through illegal, illegitimate and corrupt means. It controls 95% of the cotton seed supply and collects royalties in the form of technology fees even tough it does not have a valid patent – because Monsanto introduced Bt cotton into India illegally, before India changed its patent laws (following a WTO – TRIPS dispute), and when we did amend our patent act we introduced clause 3 (j) clearly defining that biological processes are not inventions.
ARTICLE 3(J) EXCLUDES FROM PATENTABILITY “PLANTS AND ANIMALS IN WHOLE OR IN ANY PART THEREOF OTHER THAN MICROORGANISMS; BUT INCLUDING SEEDS, VARIETIES, AND SPECIES, AND ESSENTIALLY BIOLOGICAL PROCESSES FOR PRODUCTION OR PROPAGATION OF PLANTS AND ANIMALS”.
Knowing that Monsanto was collecting illegal royalties, and that there is an epidemic of farmers suicides (300,000 farmer suicides due to a debt trap created by costly seeds and chemicals) the government has failed to act. The government failed to break Monsanto’s illegal monopoly, and it failed in its public duty to ensure a supply of safe, reliable, renewable seed for our farmers.
A Right To Information (RTI) request submitted by the Research Foundation for Science, Technology and Ecology (RFSTE) to the Central Institute for Cotton Research in Nagpur revealed that CICR has not released a single variety of cotton for the farmers of Vidarbha since Monsanto entered India’s cotton seed market.
Suddenly, after 20 years of slumber, there is a flurry of activity – in the press, in the PMO, in the Agriculture Ministry – to rush the introduction of a straight variety of Bt cotton by the CICR, claiming that it will serve the farmer. “Straight” is a word used to describe renewable varieties which are selections from farmers varieties. These farmers’ varieties have been bred in the commons and belong to the commons.
Could this sudden rush be a desperate attempt by the biotech industry and government to use the public sector as a Trojan horse to dilute and dismantle India’s Biosafety regulations? Could this be an attempt by Big Biotech to bypass the Indian Judiciary by bypassing the pending Supreme Court Case on GMO field trials? The biotech industry is using the public sector as a mask.
There are legal aspects related to GMO seeds. First is the issue of IPR’s and royalty collections. The second is the issue of Biosafety. Monsanto has violated both sets of regulation in India and must be held accountable for breaking the country’s laws. While Bt in straight varieties of cotton addresses the issues of seed costs for the future, it does not negate Monsanto’s prior violations, nor is it any different from Monsanto’s Bt when it comes to Biosafety. According to our field studies, at least 84% of the cases of farmers suicides in Vidarbha are related to debt and failure of Bt cotton crop. If the government is committed to protecting farmers’ rights and bringing justice to the farmers, it must force Monsanto to compensate farmers for illegal royalties collected on the basis of an imaginary patent, and make reparations for the hundreds of thousands of farmers it has killed by collecting these illegitimate and illegal royalties.
Insurance statisticians have put the life of a “prime aged worker”, in the US, where Monsanto is based, at a median value of USD 7 million. 84% of 300,000 suicides, 252,000, are directly attributed to Monsanto’s Bt-Cotton. By this calculation, Monsanto, in addition to the illegal royalties collected, owes the families of ‘prime aged’ working Indian farmers an amount of USD 1.764 Trillion.
Unless action is taken on this front, the talk of straight Bt varieties is a distraction from Monsanto’s criminal actions against the farmers and seed businesses of India, and the country at large. It is also an attempt to use Indian tax payers’ money and Public Institutions to open the flood gates for GMOs beyond cotton into our food – dismantling and weakening India’s Biosafety – without corporate liability.
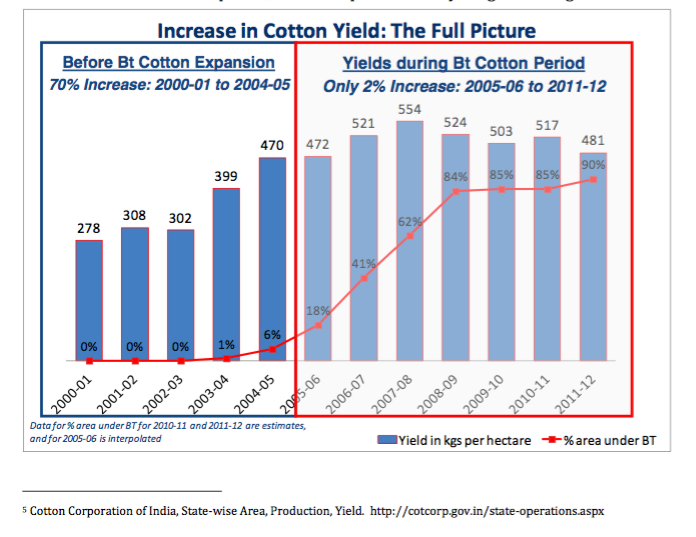
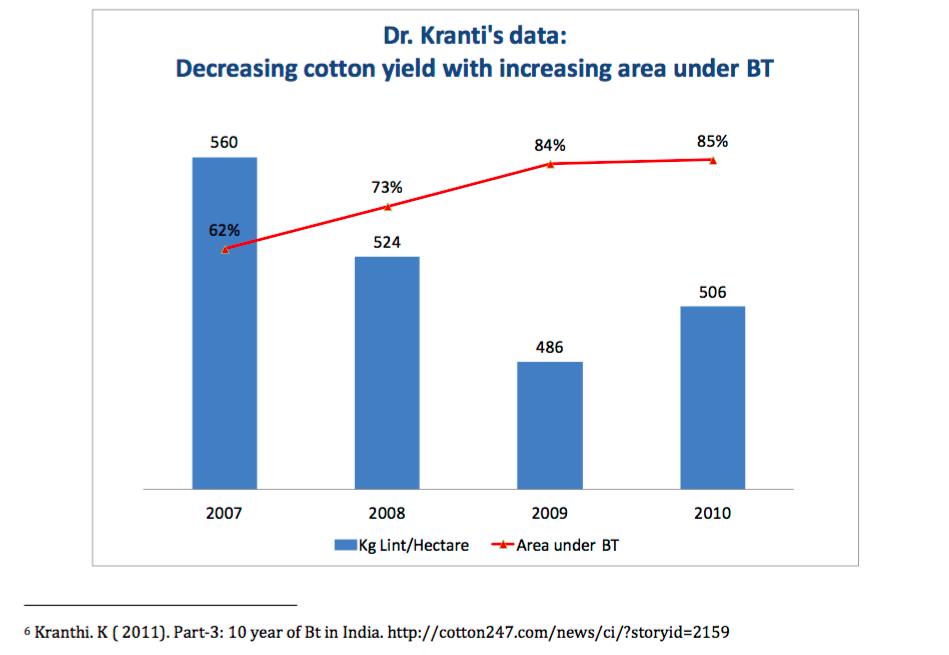
Bt – Reduced Yields Even with Increased Acreage
Monsanto has illegally collected US$ 900 million as royalty from small farmers of India. This money was charged as technology fees for Bt-technology – a technology they promised would increase cotton yields, reduce the use of pesticide and increase farmers incomes. All Bt managed to do was make money for Monsanto and push farmers to suicide. If Monsanto’s goal, with Bt, was to wage war on Indian farmers, it’s been a roaring success, in all other respects, Bt is a complete failure.
Dr. K.R. Kranthi, Director of the CICR (the same institution that, for 20 years, has failed to provide alternatives to Bt-Cotton to farmers, and now wants to introduce Bt-genes in farmers varieties of cotton), has assessed the failures of Bt and decrease in cotton yields after the introduction of Bt in India. The following tables are based on Dr Kranthi’s own data and can be found here. Why is the CICR peddling a technology which has no gain in yields, but has tremendous biosafety risks and costs to the country?
Bt-Toxification and Death of Our Soils
Surely, the CICR is aware of the failures of Bt-technology and the havoc it has wreaked on the Indian cotton sector and the cotton farmers. According to Dr. Kranthi, himself, there has also been depletion of nutrients in the soil due to repeated cultivation of Bt cotton hybrids, which draw more nutrients and water from the soil. The crop is exhibiting nutrient deficiency especially in rain-fed zones where wilt and leaf-reddening problems are also getting more severe over the years. He continues,
“The leaf hoppers showed very high levels of resistance of up to 5,000-fold to imidacloprid and other neonicotinoid insecticides in central India. The neonicotinoids were introduced barely a decade ago. Progressive nutrient (macro and micro) depletion due to the source sink relationship because of Bt-cotton after Bt-cotton hybrid cultivation. Bt-cotton hybrids utilize more nutrients and water for higher yields and profits, therefore the soils are getting progressively depleted and need more nutrient recharging.”Part III – 10 Years of Bt – Dr Keshav Kranthi
CD Mayee, of the GEAC – the agency entrusted with the regulation of biotechnology and GM field trials – and a friend to Monsanto, in his assessment, added:
“If the area under advanced transgenic seeds increases to 10 per cent in a few years from the present level of 4 per cent, the country’s fertiliser consumption will increase 107 per cent to 220 kgs per hectare (ha) from the current levels (the latest available figure 2005-06), at 106 kgs per ha.”
Located in the heart of the farmer suicide belt, being aware of the causes of these suicides and their relationship to Bt Cotton failure, why has Dr Kranthi (CICR) not released alternative seed for 20 years? Seeds that could have saved lives and alleviated the misery of Vidarbha’s cotton farmers. The CICR did not release a single cotton variety after Monsanto came to India, enabling Monsanto’s monopolistic stranglehold on Vidarbha’s cotton farmers. Why would Dr Kranthi, aware of the failures of Bt technology, be rushing the CICR to introduce Bt genes into farmers varieties of Cotton seed?
If, on the one hand, India faces pressure to change her IPR regime and on the other we face complete contamination of desi cotton by Bt, India will lose all the benefits of her cotton exports and will merely be paying Monsanto royalties to grow any cotton at all. If Monsanto has made the coffin for the Indian cotton farmer, the CICR seems intent to be the one lowering that coffin into an early grave.
Biosafety impacts of Bt GMO plants on soils and pollinators
Whether the introduction of Bt toxin into a plant (where it does not belong) is carried out by the public sector or an MNC, whether it is introduced in a straight variety or hybrid, it does not change the toxic impact Bt has on the environment and health. The Biosafety concerns for India, or any other country, remain the same.
A study of the impacts of Bt on soil ecosystems that we published in Applied Biological Research showed that beneficial soil organisms were being killed by the Bt toxin. Soil health has been destroyed by Bt cultivation. Our ongoing research shows continued reduction in the ecological activity of the soils and staggering reductions in microbial populations in Bt-toxic soils. Compared to non-Bt soils, we have found that Bt has destroyed fungi populations by 31.4%, nitrifiers by 29.6% and bacteria by 256.5% in the years since we started gathering data in 2007.
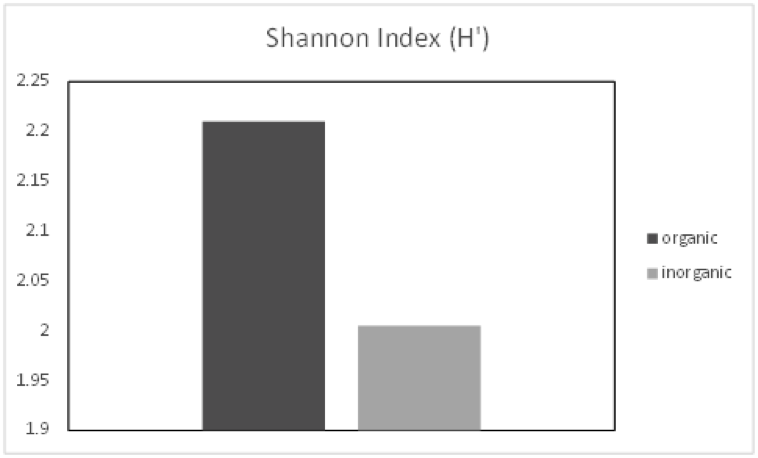
Additionally, our studies on pollinators in the Bt cotton areas show a major decline in pollinator populations in Bt fields compared to Organic fields. Diversity indices of pollinators in organic and inorganic farms show that organic farms had more species of pollinators.The Shannon diversity index (H’) of organic farms was higher than that of inorganic systems.
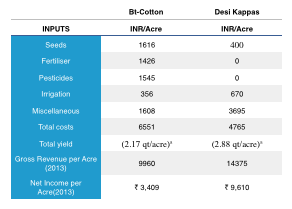
A True Cost Study of Bt-Cotton Vs Desi Kappas
Shri Radha Mohan Singh, Agriculture Minister of India, wrote the foreword for, and also released our book Wealth per Acre. In Wealth per Acre we have shown how agroecology based organic agriculture systems are far more efficient and increase the incomes of farmers. The assessments of the economics of growing cotton in India show the desi varieties, farmed organically, earn farmers much more than false promises of Bt-Cotton.
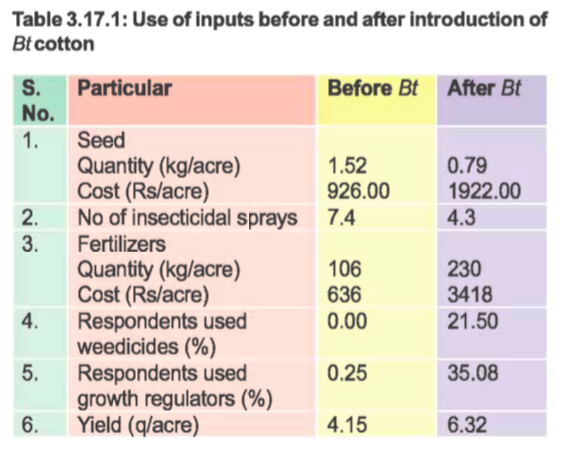
Table 3.17.1 is a table from a CICR Annual Report that shows that Dr Kranthi and the rest of CICR must be aware that cost of seed is not the only expense that increases with the use of Bt technology, whether it’s in hybrid or straight. Even compared to hybrid cotton seeds, Bt input costs are higher.
The CICR’s excuse that straight Bt seeds will be cheaper for the farmer and increase earnings is a fallacy. The development of straight variety Bt by CICR makes no sense for the farmers or the nation. Farmers earn more with their own seeds, grown organically, than with the failed Bt-technology that the CICR is attempting to force on Indian cotton farmers, instead of helping them earn more by providing organic seeds. Seeds that they can grow organically without the use of imported chemicals, earn more, and help India through exports of organic cotton.
Future Impact of BT in Straight Varieties on India’s Economy
The Biosafety issues related to Bt crops are serious. Our future ecological security and our food security depends on Biosafety. While Bt hybrids could not contaminate desi varieties, the Bt introduced in desi varieties will contaminate all desi varieties, robbing the farmers of their option to have GMO free, organic cotton seeds.
India is where cotton was domesticated. India is the leading producer of organic cotton, accounting for 74% of the world’s organic cotton supply. The global organic cotton market is estimated to be US$ 15.7 billion, with increasing demand. Without organic cotton seeds India cannot grow organic cotton. The global lack of non-GMO cotton seed is one of the most pressing issues with organic cotton today. The introduction of Bt in ‘straight’ varieties poses a grave threat to the availability of organic cotton seeds, and to India’s ability to grow and export organic cotton.
The CICR should be focusing on strengthening India’s ability to provide organic cotton and increase farmers’ earnings by working with farmers, doing participatory breeding with farmers’ varieties for an organic GMO-free seed supply, instead of attempting to force Bt – a failed technology by CICR’s own assessment. CICR should be increasing availability of desi seeds so that India can gain from her 74% market share of global organic cotton. Instead, the CICR is attempting to destroy India’s desi kappas seeds through contamination, blocking India’s opportunity in organic cotton. If our government is serious about promoting India’s rich cultural heritage, our handicrafts, our handlooms, the prime minister’s office should not be attempting to expedite the death of India’s fabric – Khaadi.
The Government of India must protect the interests of the country and of the farmers.
- Monsanto must be made to return all the money it has illegally taken from our farmers and hybrid seed companies and repatriated to the United States.
- A comprehensive Biosafety assessment of CICR Bt cotton should be carried out in accordance with the law. Biosafety framework should be strengthened keeping in mind the TEC recommendations. On those recommendations we should not introduce any GMO in a crop for which India is the centre of Diversity – like cotton.
- A plan should be made for organic breeding of organic seed for the organic sector with a focus on participatory breeding with farmers. This will protect India’s position as the leading producer of organic cotton and India’s interests in the future.
We, at Navdanya have spent the last 30 years protecting the biodiversity of our crops, spreading organic seeds and organic crops, protecting species that provide the ecological services that make agriculture possible and defending the first right of the farmer to Bija Swaraj, Seed Sovereignty – to have their own seeds, their own knowledge, to shape their own markets, their future and strengthen India by strengthening India’s farmer communities.
Additional Reading:
- 10 Years of Bt Cotton: False Hype and Failed Promises Cotton farmers’ crisis continues with crop failure and suicides
- Dr Keshav Kanthi, Director – CICR – Part III: 10 Years of Bt in India
- How Monsanto Wrote and Broke Laws to Enter India
- Hybrid seed makers seek government intervention to resolve Monsanto issue
- Wealth per Acre
__________________________________
TRANSCEND Member Prof. Vandana Shiva is a physicist, ecofeminist, philosopher, activist, and author of more than 20 books and 500 papers. She is the founder of the Research Foundation for Science, Technology and Ecology, and has campaigned for biodiversity, conservation and farmers’ rights, winning the Right Livelihood Award [Alternative Nobel Prize] in 1993. She is executive director of the Navdanya Trust.
Go to Original – vandanashiva.com
DISCLAIMER: The statements, views and opinions expressed in pieces republished here are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of TMS. In accordance with title 17 U.S.C. section 107, this material is distributed without profit to those who have expressed a prior interest in receiving the included information for research and educational purposes. TMS has no affiliation whatsoever with the originator of this article nor is TMS endorsed or sponsored by the originator. “GO TO ORIGINAL” links are provided as a convenience to our readers and allow for verification of authenticity. However, as originating pages are often updated by their originating host sites, the versions posted may not match the versions our readers view when clicking the “GO TO ORIGINAL” links. This site contains copyrighted material the use of which has not always been specifically authorized by the copyright owner. We are making such material available in our efforts to advance understanding of environmental, political, human rights, economic, democracy, scientific, and social justice issues, etc. We believe this constitutes a ‘fair use’ of any such copyrighted material as provided for in section 107 of the US Copyright Law. In accordance with Title 17 U.S.C. Section 107, the material on this site is distributed without profit to those who have expressed a prior interest in receiving the included information for research and educational purposes. For more information go to: http://www.law.cornell.edu/uscode/17/107.shtml. If you wish to use copyrighted material from this site for purposes of your own that go beyond ‘fair use’, you must obtain permission from the copyright owner.